How do I become a New York State teacher?
FACT: New York State is widely recognized for its excellent teaching force, ranking among the nation's top 10 for "teaching attractiveness" when it comes to compensation, teacher turnover, working conditions and qualifications.
TAKE THE TRADITIONAL ROUTE…
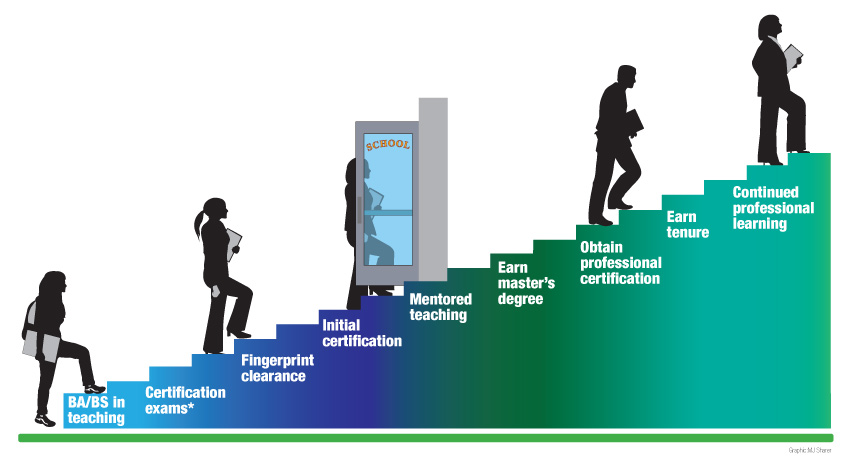
This chart (PDF version) shows New York's traditional route to licensure, where the prospective educator first earns a bachelor's degree in teacher education. The steps include:
- BA/BS in teaching
- Certification exams
- Fingerprint clearance
- Initial certification
- Mentored teaching
- Earn master's degree
- Obtain professional certification
- Earn tenure
- Continued professional learning
Bachelor's degree required
As the chart shows, a bachelor’s degree is required to become a teacher in New York state. And enrolling in a New York state teacher education program, which is pre-approved to meet the educational requirements for teacher certification, including student teaching, is the traditional route.
When choosing a program, be sure to consider the subject area (for example, science, English as a second language, or special education) and the grade level (such as elementary vs. secondary) you wish to teach. Not all teacher education programs provide training in all subject areas or grade levels.
Teacher Education Programs in New York State
Bachelor’s degree, check! Now what?
Once you’ve earned a bachelor’s degree in teacher education, the next step toward becoming a certified teacher is completing and passing a series of New York State Teacher Certification Exams.
Candidates for an initial teaching certificate must pass three main tests:
- the Educating All Students (EAS) exam;
- the edTPA; and
- the Content Specialty Test(s) in their area of certification.
For details, go to http://www.nystce.nesinc.com
Depending on the type of teaching certificate you’re seeking, other exams may also be required. Fingerprinting is the final step toward reaching the first teaching milestone: Initial certification.
Take it to the next level with professional certification.
Once you’ve earned your initial teaching certificate, professional certification is the next step. But reaching this milestone requires a return to the classroom — this time as a graduate student. You have five years to earn your master’s degree after qualifying for your initial certificate. Professional certification will also require you to have at least three years’ teaching experience in your certification area and one year of mentored teaching. Once these qualifications are met, you’re ready to apply to NYSED for professional certification.
Teaching = a lifetime of learning.
Although it’s technically the final step in the teaching journey, professional certification isn’t the end. Maintaining a professional teaching certificate requires a lifetime of learning — educators must log 100 hours of professional learning every five years.
Joining the ranks of NYS teachers takes rigor and perseverance. But it’s that commitment to excellent that makes NYS teachers among the nation’s best. Are you up for the challenge?
TAKE AN ALTERNATE ROUTE…

Already have a bachelor’s or a master’s degree?
While earning a bachelor’s degree in teacher education is the traditional route to the classroom in New York state, it’s not the only route.
If you already have a bachelor’s or a master’s degree in a non-education field, there are other options.
Transitional teaching certificates and internship teaching certificates offer candidates an alternate route to the classroom — one that allows them to earn a teaching salary while completing their graduate coursework.
What’s the difference between the two certificates?
There are several differences between the two, but the biggest is availability.
Transitional certificates are available only through select NYS-approved graduate teacher education programs, while internship teaching certificates are available through all NYS-approved graduate teacher education programs. Additionally, students must be recommended by their graduate teacher education program for an internship teaching certificate; transitional teaching certificates are available to all.
For a searchable database of approved teacher education programs, visit http://www.highered.nysed.gov/tcert/certificate/teachrecommend.html.
Additionally, students must be recommended for internship teaching certificates by their graduate teacher education program while transitional teacher certificates are available to all.
Are there different credit requirements?
Yes, there are. Transitional certificates generally allow matriculated graduate students in registered teacher education programs to start teaching, and receiving a teaching salary, generally after earning 12 credits.
Internship teaching certificates allow matriculated graduate students in registered teacher education programs to start teaching, and receiving a teaching salary, after completing roughly half their graduate program, typically about 18-21 credits.
How long do they take to finish?
Internship teaching certificates are valid for two years, are non-renewable and participants must fully complete their graduate teacher education programs during those two years. Since they don’t provide the mandated three years of teaching experience, internship teaching certificates qualify holders for an initial teaching certificate, which is valid for five years.
Under a transitional teaching certificate, participants must complete their graduate teacher education program within three-years and holders qualify for an initial certificate.
Besides a degree, are there other requirements?
Program requirements for transitional teaching certificates vary according to each college or university, but generally require a 3.0 undergraduate GPA and, for those preparing to teach at the secondary level, a major in the subject they plan to teach.
Participants must also take two NYS teacher exams before qualifying for the certification, the Content Specialty Test (CST) and the Educating All Students (EAS) exam.
Both internship teaching certificates and transitional teaching certificates require that participants have an employment offer, and supervisory support, from their school district placement. For more information about internship teaching certificates, visit http://www.highered.nysed.gov/tcert/certificate/typesofcerts/int.html.
Are teacher certification exams still required?
Yes, those holding transitional and internship teaching certificates are still required to pass three main New York State Teacher Certification Exams.
Depending on the type of teaching certificate sought, other exams may be required. Fingerprinting is also mandated.
And remember — to qualify for a transitional teaching certificate, applicants must pass the CST and EAS exams before applying.
Is that it?
Not quite. Although professional certification is technically the final step in the teaching journey, it isn’t the end.
Maintaining a professional teaching certificate requires a lifetime of learning — educators must log 100 hours of professional learning every five years.
Are there any NYC-based alternatives?
If you’re interested in teaching in New York City schools, check out the New York City Teaching Fellows Program. It’s a subsidized master’s degree fellowship targeted at increasing the number of highly trained teachers in the NYC public school system.
Fellowships include a pre-service training program, real teaching experience in NYC classrooms, and one-on-one mentoring with experienced coaches. For information, visit https://nycteachingfellows.org/.
